25 Sep 2025
Why Hydrogen?
Hydrogen isn’t just clean; it’s powerful. It packs nearly three times more energy than traditional fossil fuels like diesel. Burn it, and you get zero greenhouse gases. The only byproduct? Water.
But hydrogen’s versatility goes beyond just being a fuel. It can also be used to produce other gas and liquid fuels, making it a key player in the energy transition. There’s a catch though, hydrogen doesn’t exist freely in nature. It’s always bonded with other elements, most commonly oxygen (as water). So, to use it as fuel, we first need to break that bond.
What Makes Hydrogen Green?
Splitting hydrogen from oxygen takes energy. If that energy comes from fossil fuels, you get grey hydrogen cheap, but carbon intensive. Trap and store that carbon, and you get blue hydrogen better, but still not perfect.
The real game-changer? Green hydrogen made using renewable energy like solar or wind. No emissions. No compromise.
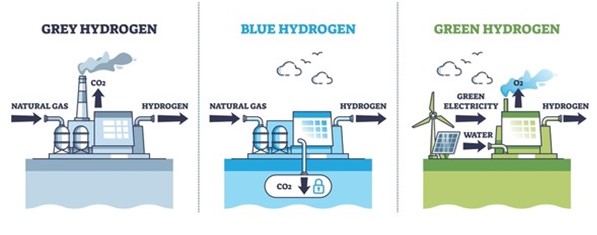
A device called an electrolyzer uses electricity to split water into hydrogen and oxygen. That’s how we get green hydrogen. Once produced, hydrogen can be compressed, stored, and transported with minimal energy loss. Later, a fuel cell reunites hydrogen with oxygen to generate electricity completing the cycle.
Green hydrogen isn’t just a clean fuel it’s a building block for other compounds that are transforming industries. Take green ammonia, for example produced by combining green hydrogen with nitrogen, it’s finding applications in glass & ceramics, concrete, steelmaking, and fertilizers.
Then there’s green methanol, made using green hydrogen and carbon dioxide. It’s being explored as a clean marine fuel, with the potential to revolutionize the global shipping industry.
Green hydrogen is also making inroads into long-distance transport especially in sectors where electrification is tough, like heavy-duty trucks, aviation, and shipping.
While Electric Vehicles are great for short distances, hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCEVs) offer longer range and faster refuelling, making them suitable for demanding applications.
Tackling Industrial Emissions
While renewables are making strides in electricity generation, industrial emissions remain a challenge. Take steel production it accounts for nearly 7% of global CO₂ emissions, largely due to its reliance on coal (which supplies ~75% of the sector’s energy).
But there’s hope. Hydrogen-based furnaces paired with electric furnaces, are emerging as a viable path to decarbonize steel.
(Source: Hitachi Energy Blog)
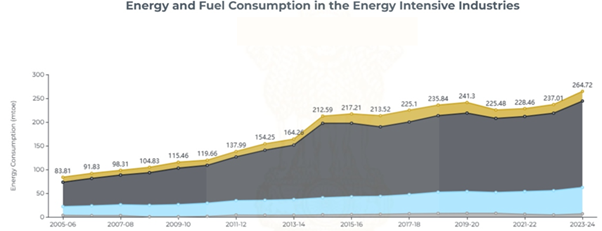
Source: NITI Aayog Energy Dashboard, as per latest available data.
India’s Net Zero Journey: Ambitious, But Achievable
India has pledged to reach Net Zero emissions by 2070. That’s a tall order for a country where nearly 70% of electricity still comes from fossil fuels like coal, oil and gas.
But progress is underway. India’s renewable energy capacity has grown from 76.37 GW in March 2014 to 226.79 GW by June 2025 a near threefold increase in just over a decade.
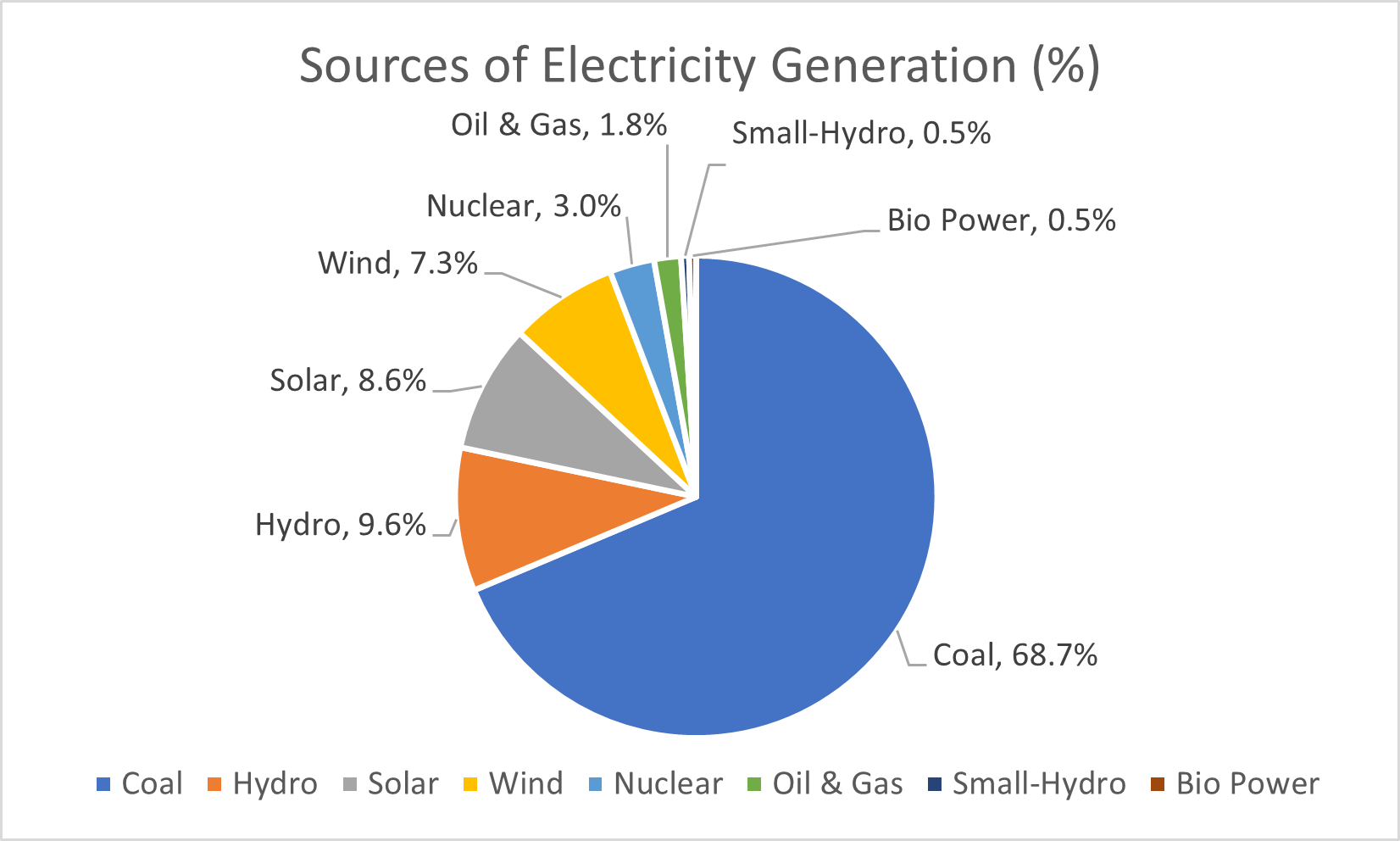
Source: NITI Aayog Energy Dashboard
India aims to become energy independent by 2047 and net zero by 2070. Green hydrogen is central to this vision. The target is 5 million metric tons of green hydrogen per year by 2030.
To support this, the government has launched the National Green Hydrogen Mission, with an outlay of ₹19,744 crore up to FY29-30. The mission offers two separate financial incentive schemes to promote domestic manufacturing of electrolysers and the production of green hydrogen.
| Particulars | Electrolysers |
Green Hydrogen/Green Ammonia |
Pilot Projects |
R&D |
Other Mission Components |
|
Incentives (Rs. Crs) |
4,440 |
13,050 |
1,466 |
400 |
388 |
Source: National Green Hydrogen Mission Portal of India
Interestingly, private sector giants are stepping up in a big way. Adani New Industries (ANIL) has announced plans to produce 2.1 mmtpa (Million Metric Tonnes per annum) of green hydrogen, while Reliance Industries (RIL) aims to scale up to 3 mmtpa by 2032. Together, these two players alone could surpass the government’s 5 mmtpa target possibly even before 2032.
(Source: Emkay Research)
The Green Hydrogen Price Puzzle
The cost of producing green hydrogen in India is gradually coming down but the journey to the target price of $1–2 per kg still looks long. Currently prices hover around $3.8 per kg, making it significantly more expensive than conventional fuels and even some international benchmarks. (Source: Emkay Research)
While India enjoys low capital and operating costs, its high cost of borrowing pushes overall expenses up. Countries like Germany and France benefit from cheaper financing, even if they lack India’s solar advantage.
To compete globally, India needs to cut costs by ~30%. Even a 10% reduction could help beat key importers like Germany.
(Data as of Apr’24. Source: Orfamerica - Decoding India's Green Hydrogen Potential)
Other countries are already offering strong incentives; U.S. is offering up to $3/kg in tax credits & Australia over $1 billion in subsidies. India’s policy support needs to match this momentum.
Real Life Applications around the world:
Green hydrogen is transforming the world right now. In Germany, hydrogen-powered trains are replacing diesel. Japan lit up the Tokyo Olympic Village using hydrogen energy. In India, Delhi’s pilot hydrogen buses are rolling, and the first hydrogen-powered train is ready for launch. Aviation leaders like Airbus are designing zero-emission aircraft, ports are testing hydrogen shipping, and British startup ZeroAvia has already built a prototype hydrogen aircraft, pushing the boundaries of clean aviation. Kawasaki, too, is making waves recently demonstrating a hydrogen combustion engine motorcycle in Japan, showing that even two-wheelers can join the hydrogen mobility movement. Meanwhile, hydrogen powered cars from Toyota (Mirai), Hyundai (Nexo), and Honda (Clarity Fuel Cell) are already available for sale, proving that hydrogen-powered cars are no longer futuristic they’re on the road today.
These breakthroughs show green hydrogen technology isn’t just a promise it’s powering a net zero future today.
India’s journey is ambitious, but with the right mix of policy support, private investment, and technological innovation, it’s well within reach.
The future is green. And hydrogen is leading the way.
MUTUAL FUND INVESTMENTS ARE SUBJECT TO MARKET RISKS, READ ALL SCHEME RELATED DOCUMENTS CAREFULLY.
The stocks/sectors mentioned do not constitute any kind of recommendation and are for information purpose only. Kotak Mahindra Mutual Fund may or may not hold position in the mentioned stock(s)/sector(s). These materials are not intended for distribution to or use by any person in any jurisdiction where such distribution would be contrary to local law or regulation. The distribution of this document in certain jurisdictions may be restricted or totally prohibited and accordingly, persons who come into possession of this document are required to inform themselves about, and to observe, any such restrictions.


