17 Oct 2025
Macaulay duration is a key concept in fixed income investing that helps investors understand the average time required to recover a bond’s investment through its cash flows. In debt mutual funds, Macaulay duration plays a crucial role in portfolio management, guiding fund selection, aligning investments with the investor’s horizon, and managing interest rate risk effectively. Understanding Macaulay Duration can assist investors in evaluating interest rate sensitivity of debt instruments.
Key Takeaways
- Macaulay duration measures the average time required to recover a bond’s investment through its cash flows.
- Modified and Effective Duration build on Macaulay duration to evaluate how bond prices respond to changes in interest rates.
- Duration helps investors select bonds or debt funds aligned with their risk tolerance and investment horizon.
- Supports portfolio immunization and risk management in volatile interest rate environments.
- Macaulay duration assumes fixed cash flows and does not account for credit, market, or liquidity risk; it is less effective for bonds with embedded options.
What is Macaulay Duration?
Macaulay duration is a measure that calculates the weighted average time an investor must hold a bond to recover its investment through cash flows. It represents the point at which the present value of all future bond payments equals the bond’s purchase price.
The Macaulay duration depends on factors such as the bond’s price, maturity, coupon rate, and yield to maturity. It is also widely used to assess a bond’s sensitivity to changes in interest rates, helping investors and portfolio managers manage interest rate risk effectively.
Benefits of Using Macaulay Duration
- Measures Interest Rate Sensitivity: Helps investors understand how changes in interest rates can affect the value of bonds or debt funds.
- Supports Portfolio Immunization: Assists in building portfolios that are protected against interest rate fluctuations.
- Guides Investment Decisions: Helps in selecting bonds or debt funds that align with the investor’s time horizon.
- Enhances Risk Management: Provides a framework to manage risks in volatile interest rate environments effectively.
Factors Affecting Macaulay Duration
- Several elements influence a bond's Macaulay duration, including its price, maturity, coupon rate, and yield to maturity:
- Time to Maturity: All else being equal, the longer a bond's maturity, the higher its duration.
- Coupon Rate: Bonds with higher coupon rates have lower durations because investors receive larger cash flows earlier.
- Interest Rates: As market interest rates rise, a bond's duration typically decreases, reducing its sensitivity to further rate changes.
- Special Features: Features like sinking funds, scheduled prepayments, or call provisions also reduce a bond's duration by shortening the expected time to receive cash flows.
Macaulay Duration Formula Explained
Macaulay duration can be calculated using the following formula:
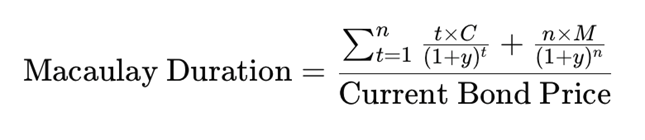
Where:
- t = Time period (in years or periods)
- C = Periodic coupon payment
- y = Periodic yield (yield per period)
- n = Total number of periods until maturity
- M = Maturity (face) value of the bond
Why Duration Matters for Debt Mutual Funds?
Interest Rate Sensitivity: Duration indicates how sensitive a debt fund’s NAV is to changes in interest rates, helping investors anticipate potential fluctuations.
Aligning Investment Horizon: It assists investors in matching their investment horizon with their risk tolerance.
Fund Selection Guidance: Duration helps in choosing debt funds that are suitable for both short term and long term financial objectives.
Difference Between Macaulay Duration and Modified Duration
|
Feature |
Macaulay Duration |
Modified Duration |
|
Definition |
Measures the weighted average time to receive all cash flows (principal and interest) from a bond. |
Measures a bond’s price sensitivity to interest rate changes, derived from Macaulay Duration. |
|
Purpose |
Shows how long it takes, on average, to recover the invested amount. |
Estimates the percentage change in bond price for a 1% change in yield. |
| Use |
Useful for understanding the time related risk of a bond. |
Widely used for interest rate risk management and in factsheets. |
|
Relationship |
Basis for calculating Modified Duration. |
Modified Duration = Macaulay Duration ÷ (1 + periodic yield) |
Classification of Debt Mutual Funds Based on Macaulay Duration
- Ultra Short Duration Fund: Invests in debt and money market instruments with a portfolio Macaulay duration between 3 to 6 months.
- Low Duration Fund: Invests in debt and money market instruments with a portfolio Macaulay duration between 6 to 12 months.
- Short Duration Fund: Invests in debt and money market instruments with a portfolio Macaulay duration between 1 to 3 years.
- Medium Duration Fund: Invests in debt and money market instruments with a portfolio Macaulay duration between 3 to 4 years.
- Medium to Long Duration Fund: Invests in debt and money market instruments with a portfolio Macaulay duration between 4 to 7 years.
- Long Duration Fund: Invests in debt and money market instruments with a portfolio Macaulay duration of more than 7 years.
- Dynamic Bond Fund: Invests across different durations depending on interest rate expectations.
- Gilt Fund with 10 Year Constant Duration: Invests a minimum of 80% in government securities, ensuring that the portfolio’s Macaulay duration is maintained at 10 years.
Macaulay Duration vs Modified & Effective Duration
- Macaulay Duration: Macaulay duration is a measure that calculates the weighted average time an investor must hold a bond to recover its investment through cash flows.
- Modified Duration: Derived from Macaulay Duration, it measures a bond's price sensitivity to changes in interest rates. This is the standard metric used to assess interest rate risk.
- Effective Duration: Used for bonds with embedded options (like callable or putable bonds). It accounts for expected changes in cash flows due to these options, providing a more accurate measure of interest rate sensitivity than Modified Duration in such cases.
Limitations of Macaulay Duration
- Fixed Cash Flow Assumption: Assumes that all cash flows are fixed, making it unsuitable for callable or putable bonds.
- Credit Risk Ignored: Does not account for credit risk or changes in the probability of default.
- Limited Risk Scope: Measures only interest rate risk and does not consider market or liquidity risk.
Conclusion
Macaulay duration is a fundamental tool for investors and portfolio managers to understand the timing and risk associated with bond investments. By calculating the weighted average time to receive a bond’s cash flows, it helps in assessing interest rate sensitivity, guiding investment decisions, and implementing portfolio immunization strategies. While it has certain limitations such as assuming fixed cash flows and not accounting for credit or market risk when used alongside Modified and Effective Duration, it provides a comprehensive framework for managing debt investments effectively.
FAQs
1) How is Macaulay duration different from maturity?
Maturity is the specific date on which a bond’s principal is repaid to the investor. It indicates only the end of the bond’s term.
Macaulay Duration is the weighted average time required to receive all cash flows from a bond, including both interest and principal. It reflects the timing and size of each payment, not just the final repayment.
2) Can Macaulay duration be negative?
No, Macaulay duration cannot be negative. It measures the weighted average time to receive a bond’s cash flows, and time periods and cash flows are always positive values. Even for bonds with embedded options or special features, the duration may be shorter but remains a positive number.
3) Does a higher coupon always shorten duration?
Bonds with higher coupon rates pay larger cash flows earlier, which reduces the weighted average time to recover the investment, thereby shortening Macaulay duration.
4) How often should I check a fund’s duration?
Investors should review a debt fund’s duration periodically. Monitoring duration helps align the fund with your investment horizon and risk tolerance, and ensures you are aware of potential NAV fluctuations due to interest rate movements.
5) What happens to duration as a bond nears maturity?
As a bond approaches its maturity date, its Macaulay duration gradually decreases because fewer cash flows remain and the investor recovers most of the principal sooner.
Disclaimers
Investors may consult their Financial Advisors and/or Tax advisors before making any investment decision.
These materials are not intended for distribution to or use by any person in any jurisdiction where such distribution would be contrary to local law or regulation. The distribution of this document in certain jurisdictions may be restricted or totally prohibited and accordingly, persons who come into possession of this document are required to inform themselves about, and to observe, any such restrictions.
MUTUAL FUND INVESTMENTS ARE SUBJECT TO MARKET RISKS, READ ALL SCHEME RELATED DOCUMENTS CAREFULLY


