30 Oct 2025
Quick commerce is like having a personal butler, always ready to fetch what you forgot, before you even realize you need it. Quick Commerce or Q-Commerce is basically e-commerce on steroids, where traditional online shopping takes days and food delivery takes hours, Q- Commerce shrinks that wait for your favourite ice cream to minutes. No wonder, brands like Swiggy, bigbasket now, JioMart#, are now a part of a day’s routine.
Traditional inventory systems can’t keep up. Q-commerce is forcing a paradigm transition in supply chain thinking, from bulk and batch to real-time and reactive which is leading to creation of purpose-built urban warehouses called as Dark Stores.
Dark stores are like underground metro lines- you don’t see them, but they move your world faster than you realize. What used to sound like sci-fi where groceries come to your doorsteps before your playlist ends is now just another weekday in urban India.
Q-commerce isn’t just shifting market share; it’s changing consumer expectations. Waiting 2 days for delivery now feels outdated when 15 minutes is the new norm.
The industry segments of quick commerce include Grocery & Fresh Food; Pharmaceuticals & Personal Care; Snacks & Beverages; Electronics & Lifestyle Essentials
Beyond speed, quick commerce’s real strength is its focus on personalization and convenience. By leveraging analytics and AI, Q-commerce platforms study consumer behavior, preferences, and purchase history to deliver highly tailored recommendations. These personalized experiences boost customer satisfaction, making shopping both faster and more relevant.
Business Models Driving the Ultra-Fast Delivery
The quick commerce ecosystem operates through distinct business models, each tailored to meet the demand & promise of seamless service#:

Invisible Engines Behind the Buzz
The two main costs in quick commerce are dark store operations, making up about 7–10% of average order value and delivery expenses, since partners are paid hourly rather than per order. As order volumes grow, these costs are spread across more units, improving operating leverage and profitability.
Example of Quick commerce operations
Source: Company reports, Bernstein analysis
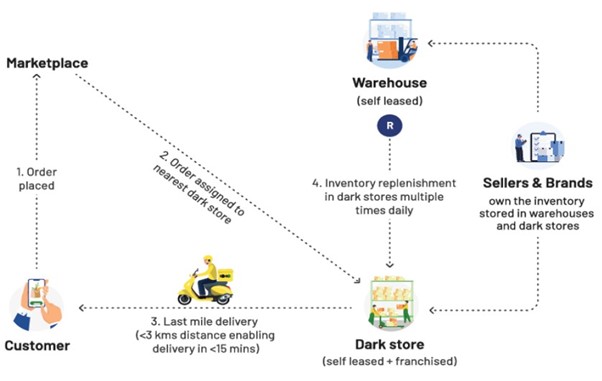
How Does a Dark Store Function?
Source: Chryseum above image is just for illustration purposes.
Number Of Dark Stores in India (FY 23 vs FY25)
|
FY 23 |
FY 24 |
FY 25 |
CAGR (FY 23-FY 25) |
|
|
Number of Q-Commerce Dark Stores in India |
1400 | 1800 | 3072 | 48.1% |
|
Average Per Store Revenue in India (In Rs Crore) |
12 | 17 | 21 | 31.4% |
Source: CareEdge Research. Note-Number of Dark Stores are calculated by the sum of major three players (Blinkit, Instamart and Zepto)# in the Q-Commerce Market.
Technology drives every step of the process: Quick commerce operations are powered by a robust tech stack that streamlines everything from inventory and shelf optimization to picker movement and rider tracking. Once an order is placed, a handheld device guides the picker to collect and pack ~6 SKU (Storage Keeping Unit)s within 1.5 minutes, while the delivery partner is simultaneously notified and routed using real-time traffic tools. The entire process, from order to doorstep, is tracked and continuously optimized to ensure speed, accuracy, and reliable ETAs for customers.
While quick commerce is often celebrated for its lightning-fast deliveries, it’s also quietly driving sustainability in retail. By leveraging advanced route optimization, retailers can reduce the number of delivery trips and cut down on fuel consumption.
Many Q-commerce platforms are also adopting eco-friendly packaging, further minimizing their environmental impact. In this way, the push for speed is increasingly going hand-in-hand with efforts to lower the sector’s carbon footprint and promote greener shopping habits.
India’s Retail Market: From Kirana Stores to Quick Commerce
The COVID-19 pandemic triggered explosive growth in quick commerce as lockdowns and safety concerns made home delivery essential, and restaurant closures pushed food delivery platforms into grocery and essentials.
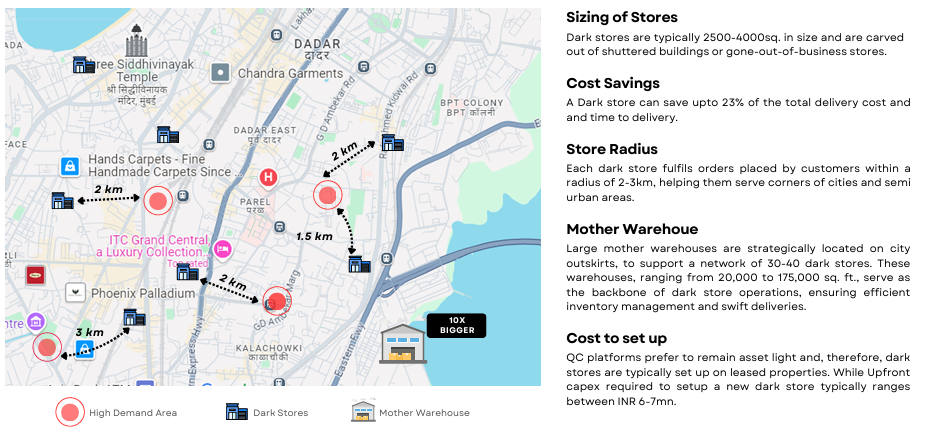
Convenience became the main driver, with Q-commerce offering better hyperlocalization (more new-age SKUs), close proximity (3km delivery radius), and ultra-fast delivery (under 15 minutes). SKU : Stock Keeping Unit which represents a unique product in store.
95% of India’s $600Bn+ grocery market is dominated by unorganized mom-and-pop stores (kirana). (Grocery market refers to the total value of all grocery-related purchases made by consumers in India — including food, beverages, household essentials, and personal care items). Their dominance is largely due to the convenience and proximity they offer to shoppers.
India’s Grocery Retail Models at a Glance:
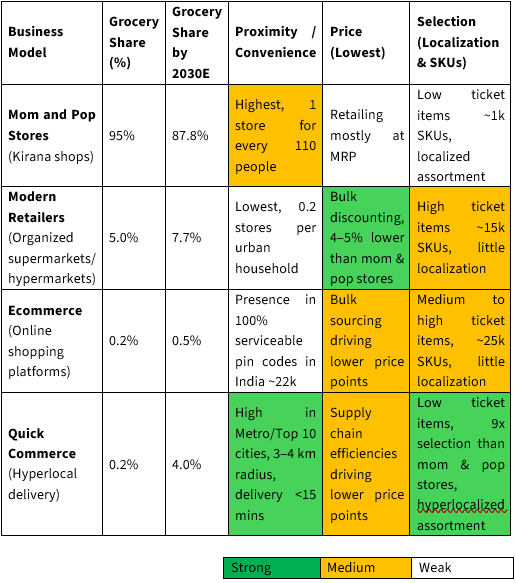
Hyperlocal delivery: a logistics model for delivering goods and services within a very small, specific geographic area in very less time
Source: Euromonitor, Redseer, company reports, Bernstein analysis and estimates
This shift highlights the gradual but significant movement of market share from traditional kirana stores to quick commerce platforms.
Quick Commerce and the Gig Economy: Jobs, Flexibility, and Impact
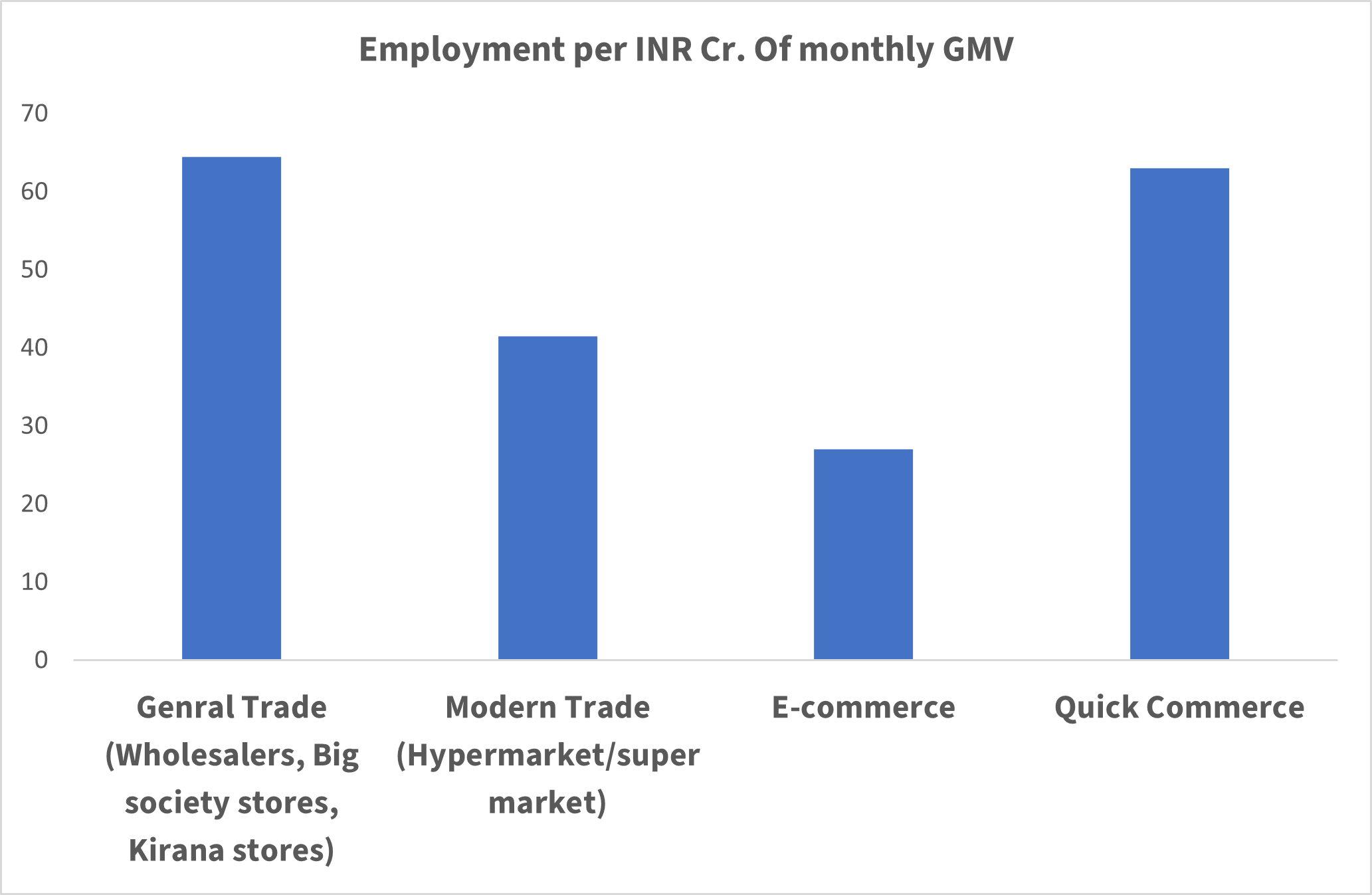
GMV: Gross merchandise value, Source: Kearney analysis
Quick commerce is driving a structural shift in employment by accelerating the move toward platform-based gig work. Many workers now take up flexible, on-demand roles, choosing part-time or full-time hours based on demand surges. Unlike centralized e-commerce hubs, quick commerce’s dark stores and micro-fulfillment centers spread jobs across urban and semi-urban areas, reducing labour market imbalances. Additionally, many delivery partners earn supplementary income by working across multiple gig platforms.
Market Size, Trends, and Growth Projections
Quick commerce in India is fuelled by the demand for instant, app-based ordering and convenience in urban lifestyles. High smartphone penetration (700M+ users) and mobile-first habits among younger consumers enable seamless digital shopping.
Structural trends such as growing urbanisation, changing consumer lifestyles, and increasing disposable income favour quick app-based shopping experiences, further fueling industry growth. High smartphone penetration (more than 85% for Indian households) and mobile-first habits among younger consumers enable seamless digital shopping.
Major FMCG brands are also embracing Q-commerce through platform-specific SKUs, premium offerings, and marketing partnerships, thereby expanding product variety and boosting average order values. Simultaneously, companies are investing heavily in dark stores, tech infrastructure, and delivery optimisation, laying the groundwork for efficient and scalable operations. Together, these factors are supporting the Q-commerce industry to become one of the key pillars in India’s evolving retail landscape.
Source: PIB
YOY QUICK COMMERCE MARKET SIZE
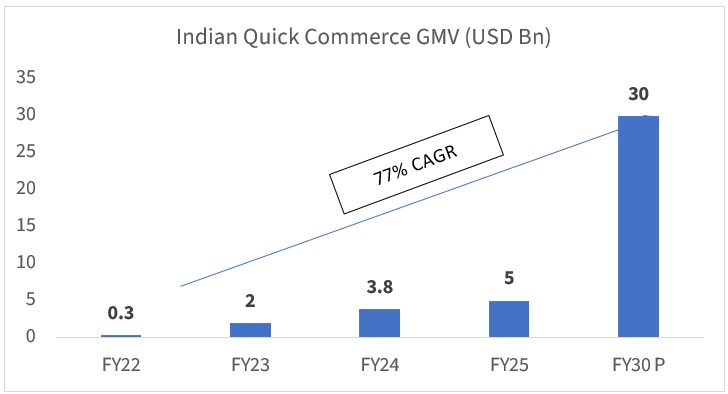
Source: Bessemer Venture Partners, P: Projected
Wrapping It Up:
The country is entering its golden era of spending and consumption, with Gen Z and millennials driving over 60% of online spending.
With only about 7% penetration of its potential market, the runway for growth is immense, offering players a chance to scale and capture new territories. Quick commerce is shaping the future of retail in an era where convenience is king, and innovation never sleeps.
Source: Bessemer Venture Partners, unified, LTI Mindtree, Kearney Analysis, CareEdge Research, Bernstein, Chryseum.
Sudheer Guntupalli, Vice President at Kotak AMC, adds - “Rising household incomes, SKU breadth, time constrained and convenience seeking customers are driving strong adoption of Quick commerce business model across both Tier I and Tier II cities. Over the previous 2-3 years, the industry is probably the top job creator in the economy - at warehouse, dark store and even rider levels. QC platforms also provide a level playing field to many small entrepreneurs to compete with established FMCG majors with distribution muscle. The most mature, over-crowded and scale markets like NCR are still growing 70%+ YoY for the market leader. This implies a multi-year runway for hyper growth in the business model"
MUTUAL FUND INVESTMENTS ARE SUBJECT TO MARKET RISKS, READ ALL SCHEME RELATED DOCUMENTS CAREFULLY.
#This is just an illustration & does not indicate any recommendation, The stocks/sectors mentioned in this slide do not constitute any recommendation and Kotak Mahindra Mutual Fund may or may not have any future position in these sectors/stocks. Use of the company brand names does not imply any affiliation with or endorsement by them or any of its holding companies, subsidiaries or affiliates and are used for illustrative purpose only. The scheme does not assure or predict any specific returns or future returns.
These materials are not intended for distribution to or use by any person in any jurisdiction where such distribution would be contrary to local law or regulation. The distribution of this document in certain jurisdictions may be restricted or totally prohibited and accordingly, persons who come into possession of this document are required to inform themselves about, and to observe, any such restrictions.


